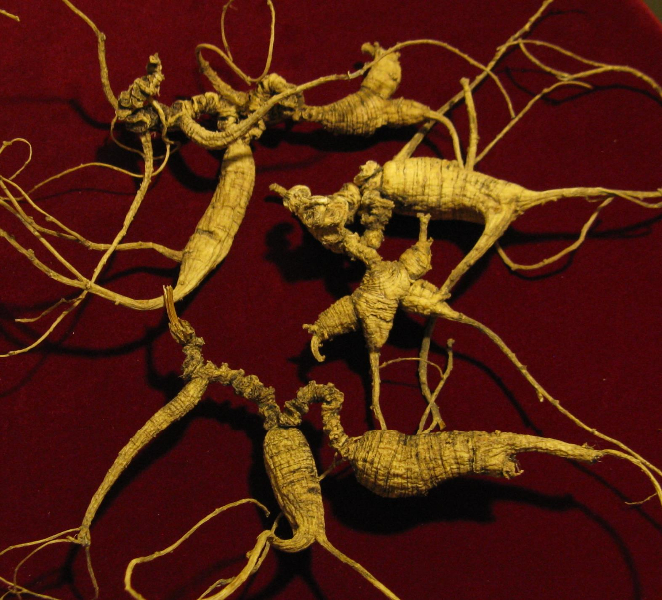
The size of the global ginseng market is poised to grow at above 4 percent annually. As the market grows, the prices are also growing especially in the US, which is the third biggest producer of the prized root. In Wisconsin, where premium US ginseng comes from, the price range in March, 2023 rose sharply.
The market is being driven by the increasing demand for natural health supplements, the growing popularity of ginseng in the food and beverage industry, and the rising awareness of the health benefits of ginseng. It is estimated that 50 percent of US adults use supplements.
The United States is the third largest producer of ginseng in the world, after China and Korea.
For a more comprehensive insight, please check the US ginseng prices
In the first quarter of 2023, restaurants in New York began taking advantage of foreign ginseng herbs from Korea to ameliorate their restaurant menus. The leading ginseng company in South Korea, Korea Ginseng Corp., now known as Cheong Kwang Jang, set up shop at a prominent ginseng eatery in New York City. It began offering what it called a herb that is beneficial to “blood circulation” and energy revitalization.
Related: Prices of Ginseng in Korea
Wild ginseng is particularly expensive because it is becoming increasingly rare. The supply is decreasing due to overharvesting and habitat loss. This means that there is less wild ginseng available, which drives up the price. Wild ginseng also takes many years to mature, which means that there is a limited supply of mature roots available.
In order to harvest the highly valued wild ginseng in the protected forests of the United States, ginseng producers/gatherers must obtain permits. These permits, offered by different districts, require a fee of $20 each. For example, as per the USDA docket for the Monongahela National Forest in West Virginia, there is a limit on the number of ginseng roots that can be harvested per day. This limit currently stands at 95 roots at a rate of less than 24 plants per day. This system ensures sustainable harvesting of ginseng while maintaining the ecological balance of the forest.